What is the HERS Index?
The Home Energy Rating System (HERS) Index is the national recognized, industry standard for measuring the energy efficiency performance of a home.
The way it works is quite simple really. A certified RESNET Home Energy Rater, like Transduction Technologies, conducts an energy rating on a home to determine its energy performance. A HERS Index score is generated based upon the results of the rating. This score gives the homeowner an indication of how energy efficient their home is in comparison to other similar homes. A lower HERS Index score means a more energy efficient home.
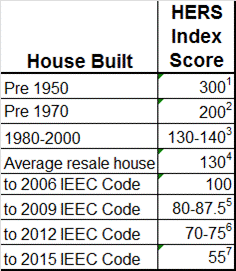
The reference point for the HERS Index is a house built to the 2004-2006 energy code, or International Energy Conservation Code (IECC) standards. A house built exactly to the 2006 IEEC standards scores 100 on the HERS Index. These figures have been determined by the U.S. Department of Energy. Each 1-point decrease in the HERS Index corresponds to a 1% reduction in energy consumption compared to the HERS Reference Home (2006 IEEC code). Likewise, every 1-point increase in the HERS Index corresponds to a 1% increase in energy consumption. So, in layman’s terms, the lower the HERS Index score, the better:
A home with a HERS Index Score of 70 is 30% more energy efficient than a standard new home
A home with a HERS Index Score of 130 is 30% less energy efficient than a standard new home
Today, in Nebraska, the current energy code is 2009 IEEC. A new home built to 2009 IEEC in Nebraska would have an average HERS score of 80-87.5. Similarly, the current national IEEC code is 2012 IEEC, where the average house would have a HERS score of 70-75. A typical resale home in the United States, that is less than 20 years old, is rated on average at 130 on the HERS Index. Older homes typically, have higher HERS Index scores. A house built before 1970 will often have a HERS score of more than 200, more than twice as much energy as the 2006 house.
To view an interactive HER model to see how much money and carbon dioxide you will save by lowering your home’s HERS score, click here.
How is my Home’s HERS Index determine? Using a computer model, a certified RESNET HERS Rater does an energy rating on your home and compares the data against a ‘reference home’– a designed-model home built to 2006 IECC of the same size and shape as your home, so your score is always relative to the size, shape and type of house you live in. Below are some of the variables taken into consideration for the rating:
All exterior wall and levels of insulation (both above and below grade)
Floor type and insulation level over unconditioned spaces (like garages or cellars)
Ceilings and roof types, orientation, and insulation
Attic, foundation and crawlspace size, condition, orientation, and insulation
Windows and door type, R-value, solar gains.
Total house air leakage
Air leakage in vents and ductwork
HVAC systems, water heating systems, and your thermostat. What are the benefits in getting a HERS Rating on my Home? A recent study(8) showed that American families earning a gross income of $50,000 experienced the following energy cost increases from 2001-2012:
2001: Avg. percentage of after-tax income spent on energy costs:12%
2005: Avg. percentage of after-tax income spent on energy costs:16%
2012: Avg. percentage of after-tax income spent on energy costs (projected):21%
A HERS Rating will accurately predict how much money you can expect to pay on your home’s energy bills, so you’ll be better able to determine your financial needs.
A HERS Rating is also a requirement for an Energy Efficient Mortgage (EEM) and/or an Energy Improvement Mortgage (EIM). The EEM is offered by FHA (HUD), VA, and Fannie Ma. When you decide to go with an EEM rather than a conventional mortgage, you benefit by:
Qualifying for a higher loan amount because of increased energy efficiency
No down payment for the home energy efficiency package
Getting a more comfortable and energy efficient home The beauty of using an energy efficient mortgage is that you get a house with a higher up-front cost, but, because you’re financing that cost and the operating expenses are lower, you end up saving money from the first month you’re in the house.
A HERS Rating is a requirement for many green building and energy efficient building standards across the country, including ENERGY STAR for Homes. Further, it can be a great way for builders and realtors to set their homes apart in a crowded real estate market. Much as miles-per-gallon fuel efficiency ratings for automobiles play an increasingly important role in car-buyers’ decisions, a Home Energy Rating may soon play an equally important role in the home buying process for home buyers across the country.
References
How is my Home’s HERS Index determine? Using a computer model, a certified RESNET HERS Rater does an energy rating on your home and compares the data against a ‘reference home’– a designed-model home built to 2006 IECC of the same size and shape as your home, so your score is always relative to the size, shape and type of house you live in. Below are some of the variables taken into consideration for the rating:
All exterior wall and levels of insulation (both above and below grade)
Floor type and insulation level over unconditioned spaces (like garages or cellars)
Ceilings and roof types, orientation, and insulation
Attic, foundation and crawlspace size, condition, orientation, and insulation
Windows and door type, R-value, solar gains.
Total house air leakage
Air leakage in vents and ductwork
HVAC systems, water heating systems, and your thermostat. What are the benefits in getting a HERS Rating on my Home? A recent study(8) showed that American families earning a gross income of $50,000 experienced the following energy cost increases from 2001-2012:
2001: Avg. percentage of after-tax income spent on energy costs:12%
2005: Avg. percentage of after-tax income spent on energy costs:16%
2012: Avg. percentage of after-tax income spent on energy costs (projected):21%
A HERS Rating will accurately predict how much money you can expect to pay on your home’s energy bills, so you’ll be better able to determine your financial needs.
A HERS Rating is also a requirement for an Energy Efficient Mortgage (EEM) and/or an Energy Improvement Mortgage (EIM). The EEM is offered by FHA (HUD), VA, and Fannie Ma. When you decide to go with an EEM rather than a conventional mortgage, you benefit by:
Qualifying for a higher loan amount because of increased energy efficiency
No down payment for the home energy efficiency package
Getting a more comfortable and energy efficient home The beauty of using an energy efficient mortgage is that you get a house with a higher up-front cost, but, because you’re financing that cost and the operating expenses are lower, you end up saving money from the first month you’re in the house.
A HERS Rating is a requirement for many green building and energy efficient building standards across the country, including ENERGY STAR for Homes. Further, it can be a great way for builders and realtors to set their homes apart in a crowded real estate market. Much as miles-per-gallon fuel efficiency ratings for automobiles play an increasingly important role in car-buyers’ decisions, a Home Energy Rating may soon play an equally important role in the home buying process for home buyers across the country.
References
- Green building consultant David Johnston
- Nate Kredich of the U.S. Green Building Council.
- RESNET. Residential Energy Services Network (RESNET). [Online] http://www.natresnet.org).
- RESNET. Residential Energy Services Network (RESNET). [Online] http://www.natresnet.org).
- http://www.energyvanguard.com/blog-building-science-HERS-BPI/bid/71518/The-2015-Energy-Code-Will-Have-a-HERS-Rating-Compliance-Path
- www.imt.org/uploads/resources/files/Fact_Sheet_on_ERI_Proposal.pdf
- Proposed for the IECC 2015 performance path for climate region 5. www.resnet.us/blog/wp-content/…/Energy-Code-188-Fact-Sheet.pdf
- www.americaspower.org/sites/default/files/Energy_Cost_Impacts_2012_FINAL.pdf
- http://www.resnet.us/energy-mortgage